Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Fibromyalgia is a disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue, sleep, memory and mood issues. Researchers believe that fibromyalgia amplifies painful sensations by affecting the way your brain processes pain signals.
Symptoms sometimes begin after a physical trauma, surgery, infection or significant psychological stress. In other cases, symptoms gradually accumulate over time with no single triggering event.
Women are more likely to develop fibromyalgia than are men. Many people who have fibromyalgia also have tension headaches, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, irritable bowel syndrome, anxiety and depression.
While there is no cure for fibromyalgia, a variety of medications can help control symptoms. Exercise, relaxation and stress-reduction measures also may help.
SYMPTOMS
Symptoms of fibromyalgia include :
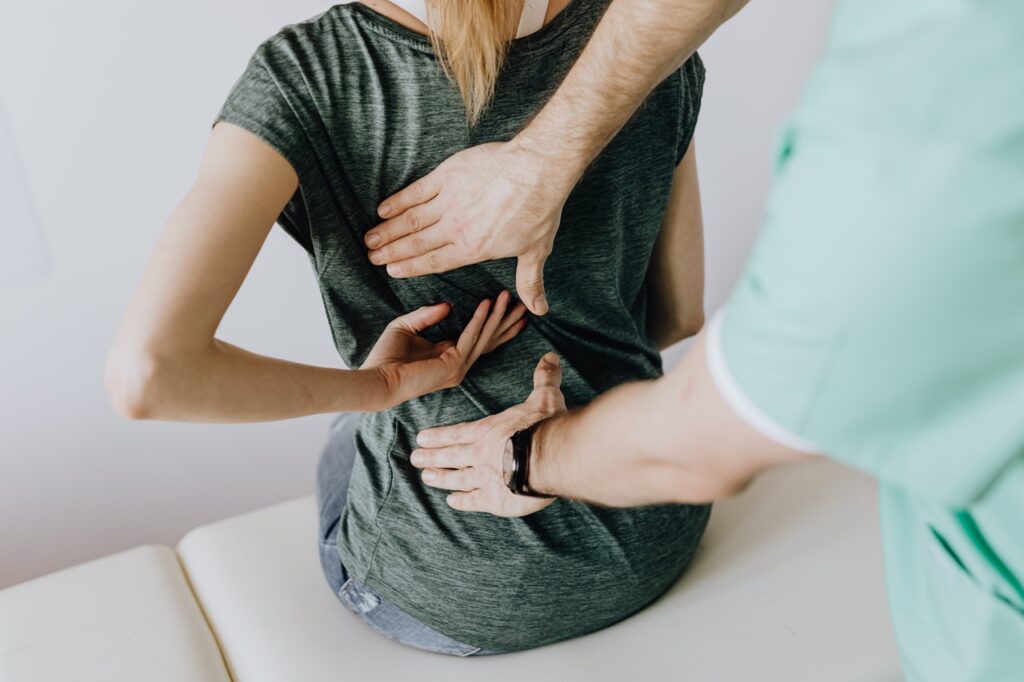
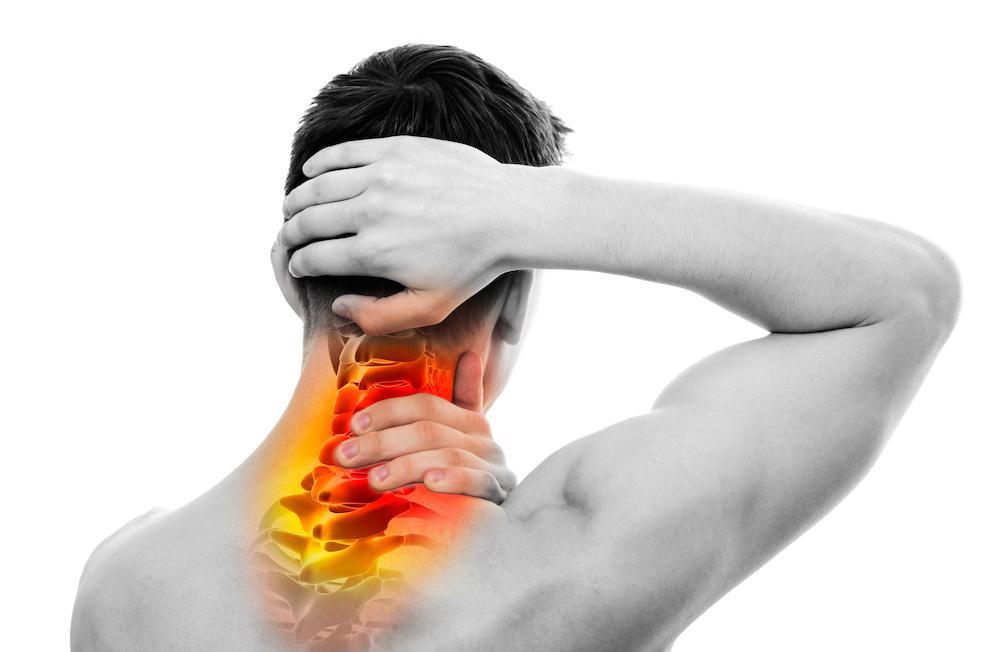
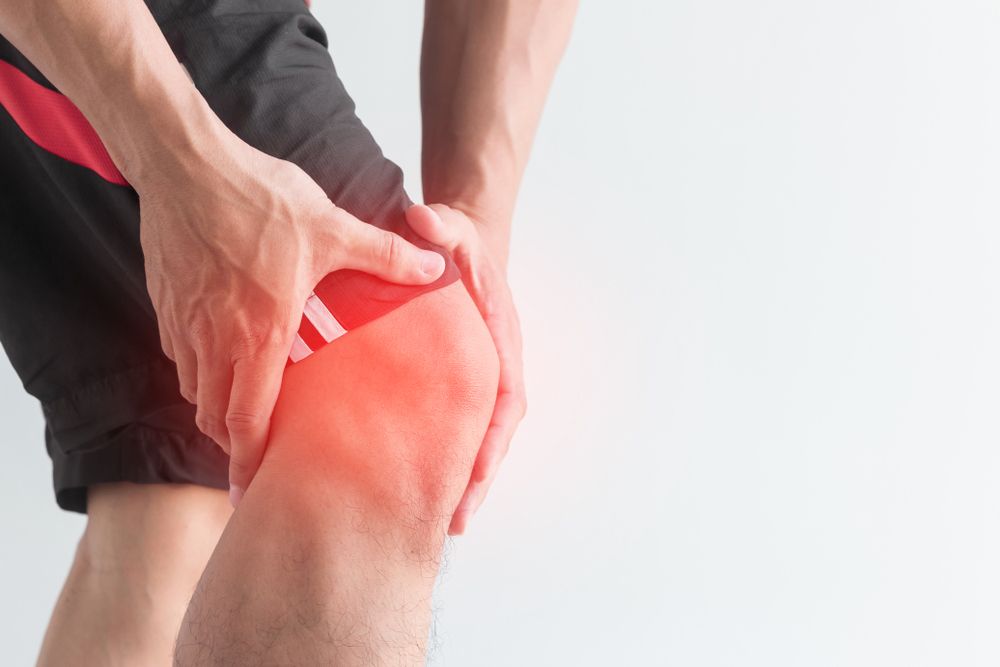
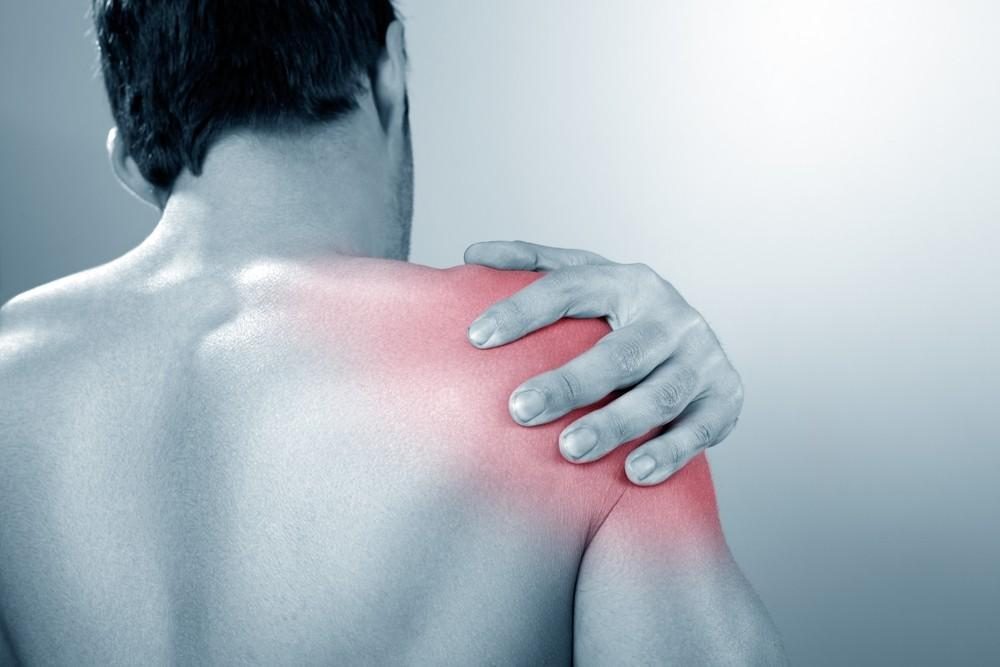
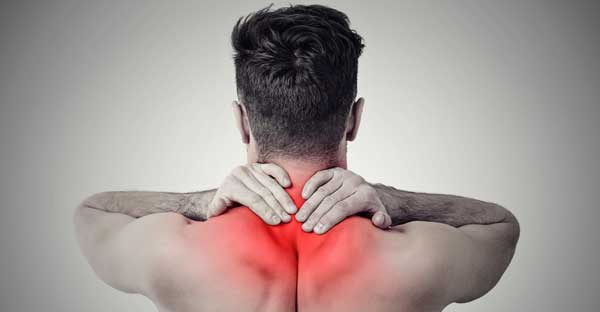
Widespread pain The pain associated with fibromyalgia often is described as a constant dull ache that has lasted for at least three months. To be considered widespread, the pain must occur on both sides of your body and above and below your waist.
Fatigue People with fibromyalgia often awaken tired, even though they report sleeping for long periods of time. Sleep is often disrupted by pain, and many patients with fibromyalgia have other sleep disorders, such as restless legs syndrome and sleep apnea.
Cognitive difficulties A symptom commonly referred to as “fibro fog” impairs the ability to focus, pay attention and concentrate on mental tasks.
Fibromyalgia often co-exists with other painful conditions, such as:
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Migraine and other types of headaches
- Interstitial cystitis or painful bladder syndrome
- Temporomandibular joint disorders
CAUSES
Doctors don’t know what causes fibromyalgia, but it most likely involves a variety of factors working together. These may include:
- Genetics : Because fibromyalgia tends to run in families, there may be certain genetic mutations that may make you more susceptible to developing the disorder.
- Infections : Some illnesses appear to trigger or aggravate fibromyalgia.
- Physical or emotional trauma : Fibromyalgia can sometimes be triggered by a physical trauma, such as a car accident. Psychological stress may also trigger the condition.
DIAGNOSIS
In the past, doctors would check 18 specific points on a person’s body to see how many of them were painful when pressed firmly. Newer guidelines don’t require a tender point exam. Instead, a fibromyalgia diagnosis can be made if a person has had widespread pain for more than three months — with no underlying medical condition that could cause the pain.
BLOOD TESTS
While there is no lab test to confirm a diagnosis of fibromyalgia, your doctor may want to rule out other conditions that may have similar symptoms. Blood tests may include :
- Complete blood count
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- Cyclic citrullinated peptide test
- Rheumatoid factor
- Thyroid function tests
TREATMENT
In general, treatments for fibromyalgia include both medication and self-care. The emphasis is on minimizing symptoms and improving general health. No one treatment works for all symptoms.
MEDICATION
Medications can help reduce the pain of fibromyalgia and improve sleep. Common choices include :
- Pain relievers : Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen (ibuprofen or naproxen sodium may be helpful. Your doctor might suggest a prescription pain reliever such as tramadol Narcotics are not advised, because they can lead to dependence and may even worsen the pain over time.
- Antidepressants : Anti-depressant may help ease the pain and fatigue associated with fibromyalgia. Your doctor may prescribe amitriptyline or the muscle relaxant cyclobenzaprine to help promote sleep.
- Anti-seizure drugs : Medications designed to treat epilepsy are often useful in reducing certain types of pain. Neuropathic pain medicine is sometimes helpful in reducing fibromyalgia symptoms,
THERAPY
A variety of different therapies can help reduce the effect that fibromyalgia has on your body and your life. Examples include:
- Physical therapy : A physical therapist can teach you exercises that will improve your strength, flexibility and stamina. Water-based exercises might be particularly helpful.
- Occupational therapy : An occupational therapist can help you make adjustments to your work area or the way you perform certain tasks that will cause less stress on your body.
- Counseling : Talking with a counsellor can help strengthen your belief in your abilities and teach you strategies for dealing with stressful situations.